Validation¶
ASaiM framework was tested on two mock metagenomic datasets from HMP metageonomes mock pilot project. These datasets are metagenomics shotgun sequences (>1,200,000 454 GS FLX Titanium single-end sequences) from a controlled community (with 22 known microbial species), available on EBI metagenomic database (SRR072232 and SRR072233).
Results obtained with ASaiM framework were intensively analyzed and compared to the ones from EBI metagenomic pipeline (version 1.0).
For these analyses, ASaiM framework was deployed on a computer with Debian GNU/Linux System, 8 cores Intel(R) Xeon(R) at 2.40 GHz and 32 Go of RAM. Size of the process in memory is stable over workflow execution (variability inferior to 40 kb). Workflow execution is relatively fast: < 5h and < 5h30 for datasets with 1,225,169 and 1,386,198 sequences respectively.
Taxonomic analyses gives a great insight into the community structure with complete, accurate and statistically supported information
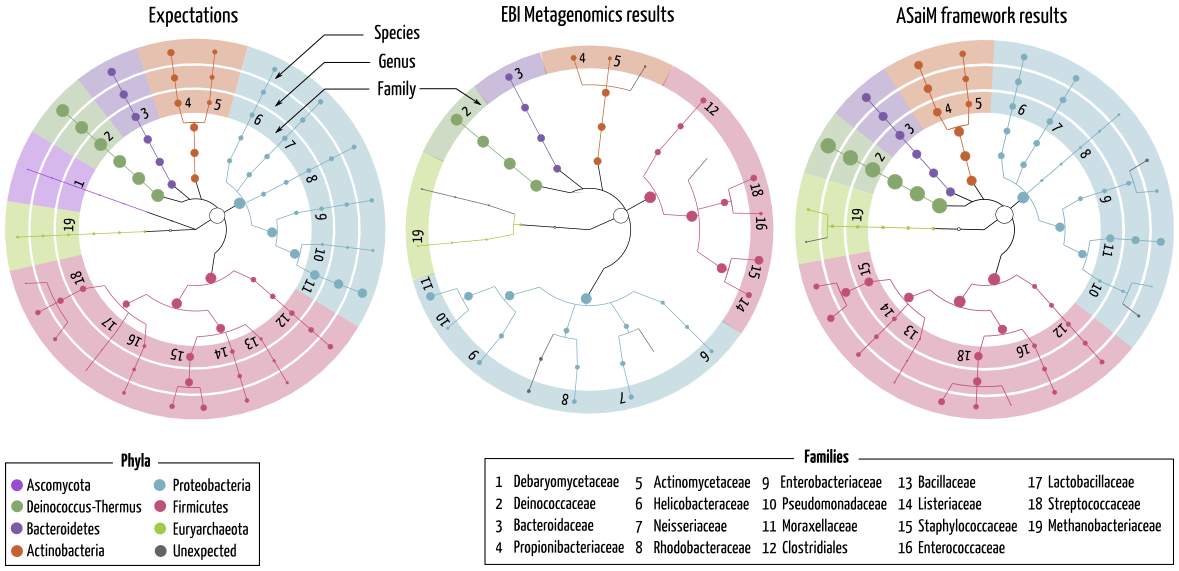
Taxonomic results for SRR072233
A broad overview of metabolic profile is available for ASaiM framework with gene families, pathways and GO slim terms. Only GO slim term information can be compared to EBI metagenomics pipeline results. It is difficult to determine which method is the best one as no expected functional information is available.
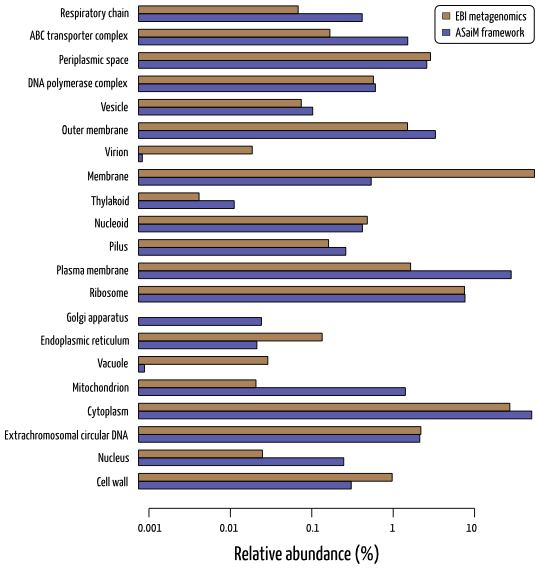
Example of functional results for SRR072233 with the relative abundance of GO slim terms related to cellular processes
The taxonomically-related functional information allows to investigate which species is involved in which metabolic functions. This type of investigation is specific to ASaiM framework, as EBI metagenomics pipeline does not provide a way to link taxonomic and functional results.
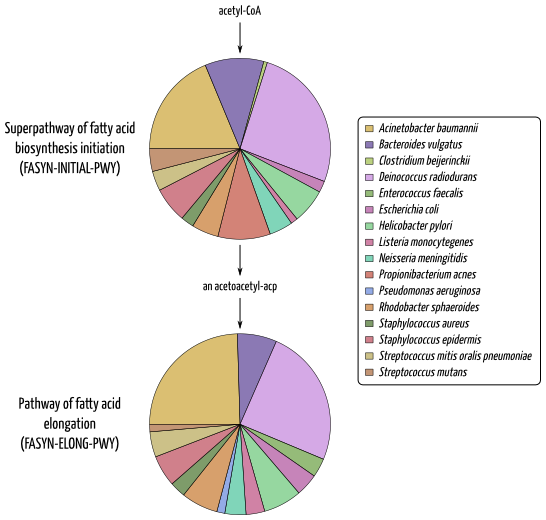
Example of investigation in which species is involved in which metabolic functions for SRR072233: Involved species and their relative involvementin fatty acid biosynthesis pathways
Further analyses and detailed comparisons of both tools and their results are organized in the report on this validation. Details about theses analyses are available on the dedicated GitHub repository.

